Section 5 - Lazy Deletion
4B.5.1 Lazy Deletion
An example of an additional member that can simplify algorithms is the inclusion of a boolean deleted member in a node class. This member would be set to true if the node has been remove()-d from the tree. As you have no doubt noticed, removal is one of the hardest parts of a tree ADT. If a fast removal is essential, one can use the proposed deleted member to completely resect this aspect of the problem by simply searching for the node and, if found, setting deleted = true. Clearly this will affect other algorithms like find() and insert(). However, in some cases, it actually speeds up those methods For example, if you attempt to insert() a node that is already there, but is marked deleted, all you have to do is change the deleted member back to false! This technique is called lazy deletion.
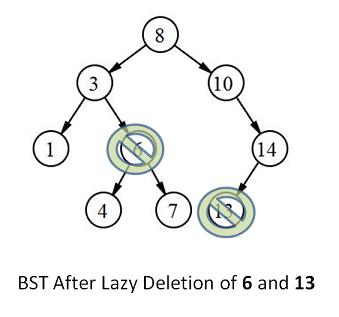
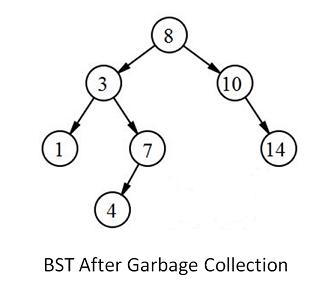
In lazy deletion, there would have to be a garbage collection mechanism that allows the client programmers the ability to prune all the deleted nodes from the tree - to really get rid of them. This does not have to be a fast function, though, since the idea is it would only be used when the system was off-line or in a non-critical state. Here are a couple ideas:
- Traverse the tree, looking for nodes that have deleted == true. When found, apply the real ("hard") remove().
- Create a second, empty tree. Then traverse the old tree, stopping only at non-deleted nodes, and when found, add them to the new tree.
4B.5.2 Some Things Required of Lazy Deletion
Lazy deletion isn't all that lazy. It trades the complexity of removal with some new complexities in other methods that have to cope with the possibility that some of the nodes still hanging in the tree are "stale". Here are a few potential treacheries that must be negotiated when implementing lazy deletion:
- The tree node type has to be adjusted to accommodate the new bool deleted member. This is short, but you cannot skip the smallest detail or nothing will work.
- Methods like find(), findMin(), operator=(), etc. must be tweaked to allow for the, now, two different ways that a node is deemed to be "not really there".
- Garbage collection must be implemented carefully, and it must be thoroughly tested.
- The old version of remove() will probably still need to be included in some form as a private utility for use by garbage collection -- assuming garbage collection is not handled by just building an entirely new tree. It should be renamed something like removeHard() (for "hard removal" in contrast to the new "soft removal" that our lazy remove() effects). removeHard() cannot be just a renamed method - it requires some tinkering.
You now have a taste for what this course is like, having immersed yourselves in a totally new data structure, the tree, from top to bottom. However, to complete the experience, you'll need to see how we apply an algorithm, called balancing, to our tree data structure to make it more efficient. This is very exciting stuff and will take us to the forefront of computer science algorithms. We'll get a glimpse of what researchers are actually doing, even today, in an attempt to make trees as fast a data structure as possible. After some great fun with this week's assignment, you will get to see what this is all about.