Section 1 - Streams

9B.1.1 Opening Streams
The objects cin and cout are examples of streams that have been instantiated and opened for you by the C++ libraries and run-time routines. You have been using them without special fanfare because they are easy to use and their use is expedited by the overloaded insertion and deletion operators, << and >>. What makes them special is that they are automatically attached to the default input device (keyboard) and the default output device (monitor console window).
This makes us optimistic that if we can figure out how to instantiate other streams associated with files instead of with the default IO devices, we might be able to get data from files and write back into files. Our optimism is warranted. Opening a file for input or output is this simple:
// open two files for reading and writing
ifstream infile("my_input_file.txt");
ofstream outfile("my_output_file.txt");
Once this is done, you can treat infile and outfile pretty much like cin and cout. Here are a couple of lines from the next program that demonstrate this:
// read 1st line from file and store into string name getline(infile, line); name = line; // ... // now write to output file outfile << name << " believes that " << x << " plus " << y << " equals " << x+y << endl
10B.1.2 The Relative Pathname to Files
Programs use either relative pathnames or absolute pathnames. A relative pathname is one that is relative to the directory that the program lives in. If we store our program and its files in the same directory we don't have to preface their names with anything. If you want to access a file somewhere else on the system you could use absolute path names that begin with "C:\documents and settings\ ...".
For this lesson, we will consider only files in our project's default directory. If your project and solution have the same name, say Foothill2, then you can easily find that directory by looking into your Visual Studio 2010 projects folder until you see the name Foothill2.
Here is the actual path to that directory in my system. I took it way back when I had VC++ 2005, but besides the version number, yours will be similar:
C:\Documents and Settings\bear\My Documents\Visual Studio 2005\Projects\15a_projects\Foothill2\Foothill2
And here is a photo of where it can be found:
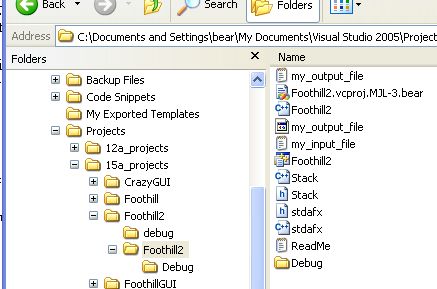
You need to know this because you are going to have to create a plain text file called "my_input_file" and save it in that folder.
10B.1.3 Creating a Text Input File
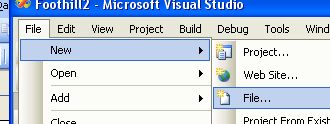
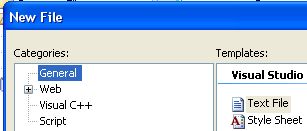
Let's manually create a text file that our program will use as input. Start an existing, or open a new, console project. From the File menu create a new file (File->New->File ...). Select a General Text File type:
 →
→ 
You will be given a blank page. Type a name on the first line and two numbers on the second. Then save it under the name my_input_file (a .txt.extension will probably be appended for you):
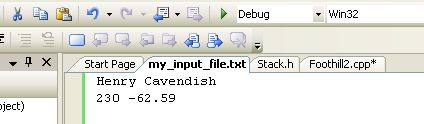
Make sure you save it in your solution's directory. If it ends up somewhere else, use the Windows explorer to move it to the folder (see my screen shot in the last section).
We are going to use this file as a source stream from which to read input.