Section 6 - STL lists (and a Sort Key Trick)
7B.6.1 STL lists
STL lists offer a very general tool for processing collections of objects. The advantage of lists over other STL containers is that they allow you to not only insert an object into the middle of the container but also remove objects from the middle - an operation vital to linked lists. Also, there are a number of algorithms that are unique to STL lists like sort(), reverse() and remove_if() to name a few. The disadvantage of lists is that they cannot be accessed randomly using bracket, [], or at() notation of vectors and deques.
We will reproduce our linked list of floats from the previous modules using the list template to assist us. Before you break open a bottle of champagne, I should tell you that there is no magic method that works like our previous insert(), which places a new element in its proper position in the list. We have to do a little work to get that functionality, even with STL lists, so be forewarned. Lists only give us something similar to our insertAfter() and deleteAfter() (through the STL list methods insert() and erase()). The logic of ordering the list must be supplied by us. Those of you who know a little more C++ might be thinking that one can use list methods such as merge() or sort() to help. True, but they also require additional tinkering to make it all work, so no matter how you look at it, the list template only gives us so much assistance.
In short, we will declare a list of floats in a single statement. This will give us all the functionality of our custom FloatList class except for the powerful insert() and remove() methods. We will write two global-scope methods insert() and remove() to accomplish this (and also a global showList() for output). In the insert() and remove() (and showList()) we will naturally use the list::iterator template to help us run through the list. In practice, you would encapsulate insert(), remove() and showList() in the proper class or even replace insert() and remove() by using merge() and/or sort(). We will do all of this is a future module. For now, we demonstrate an STL list of floats, simply as follows:
// Demo of STL list of floats (compare with our custom FloatList)
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
typedef list<float> FloatList;
void showList(FloatList &myList);
void insert(FloatList &myList, float x);
bool remove(FloatList &myList, float x);
// main method ---------------------------------------
int main()
{
FloatList myList;
int k;
float x;
// build list of 10 floats, 2 at a time (1 random and 1 k*100)
for (k = 0; k < 5; k++)
{
x = 1000 * (float)rand()/(float)RAND_MAX; // bet 0 and 1000
insert(myList, x);
insert(myList, k*100);
insert(myList, k*100); // duplicates
}
// should be sorted
showList(myList);
// remove 5 nodes (and delete them!)
for (k = 0; k < 5; k++)
{
x = k*100;
if (remove(myList, x))
cout << x << " removed\n";
else
cout << x << " not found.\n";
}
showList(myList);
if (!remove(myList, -10)) // should have no effect
cout << " -10 not in list as expected. ";
showList(myList);
return 0;
}
// Global method definitions --------------------------
void insert(FloatList &myList, float x)
{
list<float>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find a float > x
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x < *iter )
break; // found the exact place for this float
myList.insert(iter, x);
}
bool remove(FloatList &myList, float x)
{
list<float>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find or exhaust list
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x == *iter )
{
myList.erase(iter);
return true;
}
return false;
}
void showList(FloatList &myList)
{
list<float>::iterator iter;
cout << endl << "_____Here's the List_______" << endl;
for( iter = myList.begin(); iter != myList.end(); iter++)
{
cout.setf(ios::fixed);
cout.precision(3);
cout << "[" << *iter << "] ";
}
cout << endl << "_____That's all!_______" << endl << endl;
}
Here is the run:
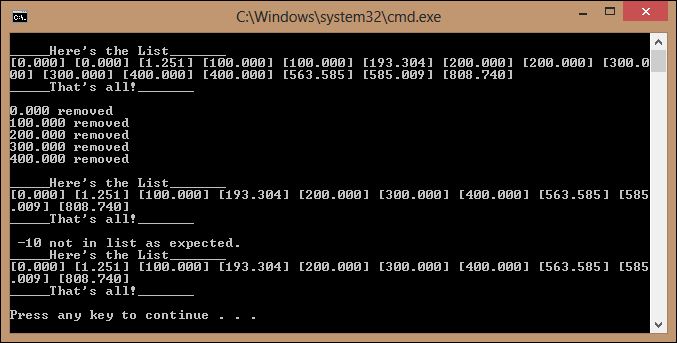
remove() vs. erase()
If you look carefully, you'll see that I intentionally added duplicates to the list so we could see that erase() only deletes one element (the first it finds). This parallels our remove()'s intention. However, you should be aware that there is an stl list::remove( itemToRemove ) method which takes an object as a parameter, not an iterator. This method removes all occurrences of itemToRemove and does not require any preliminary searching or iterators.
This is typical of many list implementations. You can use an iterator to do something local to the list, or you can use a non-iterator method that will act on the list as-a-whole.
If you call list::remove() directly, you'd see this. Or, you can write your own global-scope removeAll() which would be added to our existing global scope insert() and remove(), and which would call the list::remove(), itself. Heck, let's do both, just to firmly establish this concept in our heads.
// Demo of STL list of floats (compare with our custom FloatList)
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
typedef list<float> FloatList;
void showList(FloatList &myList);
void insert(FloatList &myList, float x);
bool remove(FloatList &myList, float x);
void removeAll(FloatList &myList, float x);
// main method ---------------------------------------
int main()
{
FloatList myList;
int k;
float x;
// build list of 10 floats, 2 at a time (1 random and 1 k*100)
// throw some duplicates in
for (k = 0; k < 5; k++)
{
x = 1000 * (float)rand()/(float)RAND_MAX; // bet 0 and 1000
insert(myList, x);
insert(myList, k*100);
insert(myList, k*100); // duplicates
}
// should be sorted
showList(myList);
// remove just the first occurrence of 100
remove(myList, 100);
// remove ALL occurrences of 200, 300
removeAll(myList, 200);
myList.remove(300);
cout << "\nafter removal:" << endl;
showList(myList);
if (!remove(myList, -10)) // should have no effect
cout << " -10 not in list as expected. ";
showList(myList);
return 0;
}
// Global method definitions --------------------------
void insert(FloatList &myList, float x)
{
list<float>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find a float > x
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x < *iter )
break; // found the exact place for this float
myList.insert(iter, x);
}
bool remove(FloatList &myList, float x)
{
list<float>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find or exhaust list
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x == *iter )
{
myList.erase(iter);
return true;
}
return false;
}
void removeAll(FloatList &myList, float x)
{
list<float>::iterator iter;
// if we wanted to return a bool true if found, we'd need to iterate
// just to detect a first occurence. But we'll let this be void
// and not worry about detecting x.
myList.remove(x);
}
void showList(FloatList &myList)
{
list<float>::iterator iter;
cout << endl << "_____Here's the List_______" << endl;
for( iter = myList.begin(); iter != myList.end(); iter++)
{
cout.setf(ios::fixed);
cout.precision(3);
cout << "[" << *iter << "] ";
}
cout << endl << "_____That's all!_______" << endl << endl;
}
/* ---------------------------- run -------------------------------
_____Here's the List_______
[0.000] [0.000] [1.251] [100.000] [100.000] [193.304] [200.000] [200.000] [300.0
00] [300.000] [400.000] [400.000] [563.585] [585.009] [808.740]
_____That's all!_______
after removal:
_____Here's the List_______
[0.000] [0.000] [1.251] [100.000] [193.304] [400.000] [400.000] [563.585] [585.0
09] [808.740]
_____That's all!_______
-10 not in list as expected.
_____Here's the List_______
[0.000] [0.000] [1.251] [100.000] [193.304] [400.000] [400.000] [563.585] [585.0
09] [808.740]
_____That's all!_______
Press any key to continue . . .
-------------------------------------------------------- */
- The Good News: This works just like our hard-fought custom FloatList class. We sacrificed nothing. (Compare the run with before - it's identical.)
- More Good News: The insert() and remove() methods were actually easier to write than before - we didn't need to stand back one node in anticipation of the awkard insertAfter() and deleteAfter() calls.
- The Bad News: We had to write methods and do some work. There are no free lunches.
7B.6.2 Multiple Sort Fields
The above analysis of a sorted list assumes we have a < operator defined for the underlying object type. With floats this is a no-brainer. They come with < already defined. We can overload < for our own class and get the same results. We can also use define and use a compareTo() if we prefer not to use operator overloading.
However, when we have data that has multiple members, any one of which we may want to use as a basis for our operator<() or compareTo(), we have to decide which one to use.
If there is only one good choice, the solution is easy. But what if we want to order the list on different members in different clients?
It works like this:
- Define some public static const ints (or enums) that the client can use to describe what kind of sort it wants. For example, in an iTunesEntry class, these constants might be called: SORT_BY_TITLE, SORT_BY_ARTIST and SORT_BY_TIME. This establishes the language for our solution.
- Define a static private member sortKey which will be exactly one of the above constants at any time. For example, if we are going to sort by artist, then the value of nSortKey will be set to the value SORT_BY_ARTIST.
- Define a static mutator method called something like setSortType() which takes one of those constants as an argument and sets the sortKey member accordingly. A client would call
iTunesEntry::setSortType( iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_ARTIST);
- Add a compareTo() method within the class and/or overload your < operator to work based on the selected sortKey.
At any time you compare two objects using syntax like obj_1 < obj_2, or if you prefer, obj_1.compareTo(obj2), it will give the answer based on the active sort key.
7B.6.3 iTunesEntry
Here is a hypothetical class, iTunesEntry, that has the following members:
class iTunesEntry
{
private:
string title;
string artist;
int totalTime;
// ... rest of class omitted
}
There are two strings and one int, and we might want our list sorted by the artist's name (artist) one day, on the title (title) on another day and the play time (totalTime) on yet a third day. Following the above plan, we first define the static int symbols and the private static as in steps 1 and 2:
class iTunesEntry
{
// ... various members, then
public:
static enum SortType { SORT_BY_TITLE, SORT_BY_ARTIST, SORT_BY_TIME };
private:
static SortType sortKey;
// ... then the rest
};
The static sortKey is the member that remembers what our sort key is at any given moment. We could define our sort types using static const int, but doing so with more than two or three constants is tedious. Therefore, we often use the enum type, which accomplishes the exact same thing - enums are ints. The above syntax for the enum SortType causes SORT_BY_TITLE = 0, SORT_BY_ARTIST = 1, etc. We covered all this in the first week if you need a refresher.
We now know what to call the "idea" of wanting to sort by artist: we call it iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_ARTIST. The client can use this same symbol when it wants to talk to our class about the sort type it wishes to use. Also, we have to give the sortKey member an initial value. As a static, this must be done outside the prototype:
iTunesEntry::SortType iTunesEntry::sortKey = iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_ARTIST;
So far, so good. Next, step 3: define a static mutator. This can be used by any client to change the value of sortKey. Like any good mutator, it must filter bad data.
bool iTunesEntry::setSortType( iTunesEntry::SortType which_type )
{
switch (which_type)
{
case SORT_BY_TITLE:
case SORT_BY_ARTIST:
case SORT_BY_TIME:
sortKey = whichType;
return true;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
Step 4 completes the picture: we have to make sure this member is actually used when we do a comparison. At a minimum, add a compareTo() method to the class (if you have access -- otherwise, you'll need to subclass or make it a global scope method). Study this method very carefull, because it is the heart of the flexibls sort key concept.
int iTunesEntry::compareTo(iTunesEntry &other)
{
string thisName, otherName;
switch (sortKey)
{
case SORT_BY_TITLE:
if (title < other.title) // < already defined for string
return -1;
else if (other.title < title)
return +1;
else
return 0;
break;
case SORT_BY_ARTIST:
// get last name from string
// stack the last name before the first - no worries about trailing last nm
thisName = getArtistLastName() + artist;
otherName = other.getArtistLastName() + other.getArtist();
if (thisName < otherName) // < already defined for string
return -1;
else if (otherName < thisName)
return +1;
else
return 0;
break;
case SORT_BY_TIME:
return (totalTime - other.totalTime);
break;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
A client would use this compareTo() in its sorts, list insertion searches, etc.
If we attempt to use certain stl class methods, or if we write our own methods that implicitly use the < operator on iTunesEntry objects, we must also overload the < operator. We'll do this as a global scope method rather than a member method, just to demonstrate that you can do this outside the class. This implementation makes use of a prior compareTo() to avoid code duplication.
bool operator< (iTunesEntry &me, iTunesEntry &other)
{
return me.compareTo(other) < 0;
}
This could be defined directly, without recourse to compareTo() if one did not exist. Just move the body of the compareTo(), above, into this method definition and make necessary syntax adjustments.
operator==()
Finally, an important note about the == operator. Typically, this is not about ordering, but about member-by-member comparisons. You should be well aware of this by now. Why bring it up in a discussion about ordering? On occasion, one might wish the == operator to be defined in terms of compareTo(), which is defined in terms of the sortKey. Understand that this is a weaker equality than member-wise equality, and if you don't understand what I mean, think about it and discuss it in the forums.
However you define operator==(), you should define it whenever you use stl classes like list. Why? Becuase the class template will normally use your operator==() to search for the item to remove(), to cite one example, and if you don't define it, you'll get a compiler error. Worse still, the error will land you in the stl list class file and confuse you. Here is an example == operator implementation, which uses the standard member-wise comparison.
// don't use & because stl wants == overloaded with val, not ref param
bool operator==(iTunesEntry me, iTunesEntry other)
{
if ( me.getTitle() != other.getTitle() )
return false;
if ( me.getArtist() != other.getArtist() )
return false;
if ( me.getTotalTime() != other.getTotalTime() )
return false;
return true;
}
Well, we now have set up our iTunesEntry class to have a totally flexible < operator. After that, you can build >, <=, >=, etc. on top of these methods. Typically, you can get by with just the < operator.
The client changes the sort key using one simple statement:
// set the sort key to song duration iTunesEntry::setSortType(iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_TIME);
Once this is done, we can apply any function or algorithm that uses the < operator, and it will be done based on time ordering.
7B.6.4 iTunes Client With Multiple Sort Keys
Here is an example client that uses the above technique. You can ignore the first part that reads the iTunesEntry data from the file. Concentrate on the methods that we have modified from the float version. We made some minor adjustments so that they work now with iTunesEntry objects.
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// class iTunesEntryReader source not included here so this will not run as-is
iTunesEntry prototype -----------------------------------------------------------------
class iTunesEntry
{
private:
string title;
string artist;
int totalTime;
public:
static const int MIN_STR_LENGTH;
static const int MAX_STR_LENGTH;
static const int MIN_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC;
static const int MAX_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC;
static const int DEFAULT_PLAY_TIME;
static const string DEFAULT_STRING;
iTunesEntry();
iTunesEntry(string nm, string art, int btrt, int tTime);
// mutators
bool setTitle(string s_arg);
bool setArtist(string s_arg);
bool setTotalTime(int tTime);
// accessors
string getTitle() { return title; }
string getArtist() { return artist; }
int getTotalTime() { return totalTime; }
string toString();
// comparator tools
// could use static const int, instead:
public:
static enum SortType { SORT_BY_TITLE, SORT_BY_ARTIST, SORT_BY_TIME };
private:
static SortType sortKey;
public:
static bool setSortType( iTunesEntry::SortType which_type );
int compareTo(iTunesEntry &other);
string getArtistLastName();
};
// global scope operator utilities a client could typically add to a class
bool operator<(iTunesEntry &me, iTunesEntry &other);
bool operator==(iTunesEntry me, iTunesEntry other);
// ----------- prototypes -------------
typedef list<iTunesEntry> TunesList;
void showList(TunesList &myList);
void insert(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x);
bool remove(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x);
void removeAll(TunesList &myList, float x);
// main method ---------------------------------------
int main()
{
TunesList myList;
// some structures and file reading utilities not explained here
iTunesEntryReader tunesInput("itunes_file.txt");
int arraySize;
arraySize = tunesInput.getNumTunes();
// set the sort key to song duration
iTunesEntry::setSortType(iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_TIME);
// build the list. It should automatically go in by song duration
for (int k = 0; k < arraySize; k++)
insert(myList, tunesInput[k]);
// should be sorted by duration
showList(myList);
// now do it again by title
myList.clear();
iTunesEntry::setSortType(iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_TITLE);
// build the list. It should automatically go in alphabetically by title
for (int k = 0; k < arraySize; k++)
insert(myList, tunesInput[k]);
// should be sorted by title
showList(myList);
return 0;
}
// Global method definitions --------------------------
void insert(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x)
{
list<iTunesEntry>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find a tune > x
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x < *iter )
break; // found the exact place for this float
myList.insert(iter, x);
}
bool remove(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x)
{
list<iTunesEntry>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find or exhaust list
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x == *iter )
{
myList.erase(iter);
return true;
}
return false;
}
void removeAll(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x)
{
// if we wanted to return a bool true if found, we'd need to iterate
// just to detect a first occurence. But we'll let this be void
// and not worry about detecting x.
myList.remove(x);
}
void showList(TunesList &myList)
{
list<iTunesEntry>::iterator iter;
cout << endl << "_____Here's the List_______" << endl;
for( iter = myList.begin(); iter != myList.end(); iter++)
{
cout << "[" << iter->toString() << "] " << endl;
}
cout << endl << "_____That's all!_______" << endl << endl;
}
The Run
_____Here's the List_______ [Our Big Break", by Veggie Tales Duration: 69] [Bullhead's Psalm", by Blue Record Duration: 79] [Bach: Suite for Cello No. 1 in G Major Prelude", by Yo-yo Ma Duration: 141] [Tico-Tico No Fuba", by Caraivana Duration: 147] [Simple Gifts", by Yo-yo Ma Duration: 154] [Ogeechee Hymnal", by Blue Record Duration: 155] [France Chance", by Ry Cooter Duration: 168] [This Will Be", by Natalie Cole Duration: 171] [Well That's All Right", by Howlin' Wolf Duration: 175] [Alimony", by Ry Cooter Duration: 175] [Feeling Good", by Nina Simone Duration: 177] [Everybody's In The Mood", by Howlin' Wolf Duration: 178] [I Can't Quit You Baby", by John Lee Hooker Duration: 182] [Donuts for Benny", by Veggie Tales Duration: 184] [The Other Woman", by Nina Simone Duration: 186] [Hobo Blues", by John Lee Hooker Duration: 187] [Watch the Girl", by The Rubyz Duration: 192] [Te Amo Tanto", by AOL Dejando Huella Duration: 192] [Twelve Sticks", by Reverend Gary Davis Duration: 194] [Lil' Crips", by Snoop Dog Duration: 195] [Rip It Up", by Jet Duration: 200] [Ladies and Gentleman", by The Rubyz Duration: 201] [The Road", by Aaron Watson Duration: 204] [My Girlfriend", by Sean Kingston Duration: 204] [Dime Si te Vas Con El", by AOL Dejando Huellas Duration: 204] [Good Life", by Kanye West Duration: 207] [Hot Cha", by Roy Buchanan Duration: 208] [Shuffleboard", by Jeff Golub Duration: 210] [Unforgettable", by Natalie Cole Duration: 211] [Samson and Delilah", by Reverend Gary Davis Duration: 216] [Think About It", by Snoop Dog Duration: 217] [Give It All U Got", by Lil Jon Duration: 218] [Quitter", by Carrie Underwood Duration: 220] [Something to Talk About", by Bonnie Raitt Duration: 227] [Russian Roulette", by Rihanna Duration: 228] [Take Your Shirt Off", by T-Pain Duration: 228] [Monkey Wrench", by Foo Fighters Duration: 230] [I'm Just a Prisoner", by Janiva Magness Duration: 230] [I Blew Up The United States", by Was (Not Was) Duration: 230] [Luka", by Suzanne Vega Duration: 231] [Small Blue Thing", by Suzanne Vega Duration: 235] [Cowboy Casanova", by Carrie Underwood Duration: 236] [Fire Burning", by Sean Kingston Duration: 239] [What We Talkin' About", by Jay-Z Duration: 243] [Noites Cariocas", by Caraivana Duration: 252] [In a Sentimental Mood", by John Coltrane Duration: 256] [Gangsta Luv", by Snoop Dogg Duration: 257] [Timothy", by Jet Duration: 260] [All My Life", by Foo Fighters Duration: 263] [Lizard Skin", by Terra Incogni Duration: 270] [You Were Never Mine", by Janiva Magness Duration: 276] [Empire State of Mind", by Jay-Z Duration: 276] [Kid Charlemagne", by Steely Dan Duration: 278] [Pretending", by Eric Clapton Duration: 283] [The Bit", by Mastadon Duration: 295] [Clone", by Terra Incognita Duration: 298] [Fish Fare", by Jeff Golub Duration: 299] [Bad Love", by Eric Clapton Duration: 308] [Black Cow", by Steely Dan Duration: 310] [Stronger", by Kanye West Duration: 311] [Medieval Overture", by Return to Forever Duration: 313] [Rockit", by Herbie Hancock Duration: 325] [I Can't Make You Love Me", by Bonnie Raitt Duration: 331] [That's The Homie", by Snoop Dogg Duration: 343] [Where Did Your Heart Go?", by Was (Not Was) Duration: 347] [Oblivion", by Mastadon Duration: 348] [Haitian Divorce", by Steely Dan Duration: 351] [Goin' On", by Jeff Golub Duration: 356] [Blues On the Corner", by McCoy Tyner Duration: 367] [Pirate Jenny", by Nina Simone Duration: 402] [Monk/Trane", by John Patitucci Duration: 434] [Green Onions", by Roy Buchanan Duration: 443] [Sonny Side", by John Patitucci Duration: 445] [Nefertiti", by Herbie Hancock Duration: 451] [A Love Supreme Part 1", by John Coltrane Duration: 462] [Afro Blue", by McCoy Tyner Duration: 742] [Brahms: Symphony No. 4 in E Minor Op. 98", by Berliner Philharmoniker Duration: 800] [Brahms: Symphony No. 1 in C Minor Op. 68", by Berliner Philharmoniker Duration: 839] [Chameleon", by Herbie Hancock Duration: 941] _____That's all!_______ _____Here's the List_______ [A Love Supreme Part 1", by John Coltrane Duration: 462] [Afro Blue", by McCoy Tyner Duration: 742] [Alimony", by Ry Cooter Duration: 175] [All My Life", by Foo Fighters Duration: 263] [Bach: Suite for Cello No. 1 in G Major Prelude", by Yo-yo Ma Duration: 141] [Bad Love", by Eric Clapton Duration: 308] [Black Cow", by Steely Dan Duration: 310] [Blues On the Corner", by McCoy Tyner Duration: 367] [Brahms: Symphony No. 1 in C Minor Op. 68", by Berliner Philharmoniker Duration: 839] [Brahms: Symphony No. 4 in E Minor Op. 98", by Berliner Philharmoniker Duration: 800] [Bullhead's Psalm", by Blue Record Duration: 79] [Chameleon", by Herbie Hancock Duration: 941] [Clone", by Terra Incognita Duration: 298] [Cowboy Casanova", by Carrie Underwood Duration: 236] [Dime Si te Vas Con El", by AOL Dejando Huellas Duration: 204] [Donuts for Benny", by Veggie Tales Duration: 184] [Empire State of Mind", by Jay-Z Duration: 276] [Everybody's In The Mood", by Howlin' Wolf Duration: 178] [Feeling Good", by Nina Simone Duration: 177] [Fire Burning", by Sean Kingston Duration: 239] [Fish Fare", by Jeff Golub Duration: 299] [France Chance", by Ry Cooter Duration: 168] [Gangsta Luv", by Snoop Dogg Duration: 257] [Give It All U Got", by Lil Jon Duration: 218] [Goin' On", by Jeff Golub Duration: 356] [Good Life", by Kanye West Duration: 207] [Green Onions", by Roy Buchanan Duration: 443] [Haitian Divorce", by Steely Dan Duration: 351] [Hobo Blues", by John Lee Hooker Duration: 187] [Hot Cha", by Roy Buchanan Duration: 208] [I Blew Up The United States", by Was (Not Was) Duration: 230] [I Can't Make You Love Me", by Bonnie Raitt Duration: 331] [I Can't Quit You Baby", by John Lee Hooker Duration: 182] [I'm Just a Prisoner", by Janiva Magness Duration: 230] [In a Sentimental Mood", by John Coltrane Duration: 256] [Kid Charlemagne", by Steely Dan Duration: 278] [Ladies and Gentleman", by The Rubyz Duration: 201] [Lil' Crips", by Snoop Dog Duration: 195] [Lizard Skin", by Terra Incogni Duration: 270] [Luka", by Suzanne Vega Duration: 231] [Medieval Overture", by Return to Forever Duration: 313] [Monk/Trane", by John Patitucci Duration: 434] [Monkey Wrench", by Foo Fighters Duration: 230] [My Girlfriend", by Sean Kingston Duration: 204] [Nefertiti", by Herbie Hancock Duration: 451] [Noites Cariocas", by Caraivana Duration: 252] [Oblivion", by Mastadon Duration: 348] [Ogeechee Hymnal", by Blue Record Duration: 155] [Our Big Break", by Veggie Tales Duration: 69] [Pirate Jenny", by Nina Simone Duration: 402] [Pretending", by Eric Clapton Duration: 283] [Quitter", by Carrie Underwood Duration: 220] [Rip It Up", by Jet Duration: 200] [Rockit", by Herbie Hancock Duration: 325] [Russian Roulette", by Rihanna Duration: 228] [Samson and Delilah", by Reverend Gary Davis Duration: 216] [Shuffleboard", by Jeff Golub Duration: 210] [Simple Gifts", by Yo-yo Ma Duration: 154] [Small Blue Thing", by Suzanne Vega Duration: 235] [Something to Talk About", by Bonnie Raitt Duration: 227] [Sonny Side", by John Patitucci Duration: 445] [Stronger", by Kanye West Duration: 311] [Take Your Shirt Off", by T-Pain Duration: 228] [Te Amo Tanto", by AOL Dejando Huella Duration: 192] [That's The Homie", by Snoop Dogg Duration: 343] [The Bit", by Mastadon Duration: 295] [The Other Woman", by Nina Simone Duration: 186] [The Road", by Aaron Watson Duration: 204] [Think About It", by Snoop Dog Duration: 217] [This Will Be", by Natalie Cole Duration: 171] [Tico-Tico No Fuba", by Caraivana Duration: 147] [Timothy", by Jet Duration: 260] [Twelve Sticks", by Reverend Gary Davis Duration: 194] [Unforgettable", by Natalie Cole Duration: 211] [Watch the Girl", by The Rubyz Duration: 192] [Well That's All Right", by Howlin' Wolf Duration: 175] [What We Talkin' About", by Jay-Z Duration: 243] [Where Did Your Heart Go?", by Was (Not Was) Duration: 347] [You Were Never Mine", by Janiva Magness Duration: 276] _____That's all!_______ Press any key to continue . . .
Note that the first list is ordered by time, and the second by title, just as we had expected.
Also notice that, besides changing the type parameter from float to iTunesEntry, we did not touch the insert() or remove() methods. So these can easily be turned into function templates and never written again. Wow.
A More Complete Listing
Here is the listing, but it does not contain the necessary class that reads the data from a file, so you won't be able to run it, as is. We'll run it in CS 2C. However, this contains all the machinery necessary to any potential assigned lab.
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// class iTunesEntryReader source not included here so this will not run as-is
// iTunesEntry prototype -----------------------------------------------------------------
class iTunesEntry
{
private:
string title;
string artist;
int totalTime;
public:
static const int MIN_STR_LENGTH;
static const int MAX_STR_LENGTH;
static const int MIN_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC;
static const int MAX_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC;
static const int DEFAULT_PLAY_TIME;
static const string DEFAULT_STRING;
iTunesEntry();
iTunesEntry(string nm, string art, int btrt, int tTime);
// mutators
bool setTitle(string s_arg);
bool setArtist(string s_arg);
bool setTotalTime(int tTime);
// accessors
string getTitle() { return title; }
string getArtist() { return artist; }
int getTotalTime() { return totalTime; }
string toString();
// comparator tools
// could use static const int, instead:
public:
static enum SortType { SORT_BY_TITLE, SORT_BY_ARTIST, SORT_BY_TIME };
private:
static SortType sortKey;
public:
static bool setSortType( iTunesEntry::SortType which_type );
int compareTo(iTunesEntry &other);
string getArtistLastName();
};
// global scope operator utilities a client could typically add to a class
bool operator<(iTunesEntry &me, iTunesEntry &other);
bool operator==(iTunesEntry me, iTunesEntry other);
// ----------- prototypes -------------
typedef list<iTunesEntry> TunesList;
void showList(TunesList &myList);
void insert(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x);
bool remove(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x);
void removeAll(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x);
// main method ---------------------------------------
int main()
{
TunesList myList;
// some structures and file reading utilities not explained here
iTunesEntryReader tunesInput("itunes_file.txt");
int arraySize;
arraySize = tunesInput.getNumTunes();
// set the sort key to song duration
iTunesEntry::setSortType(iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_TIME);
// build the list. It should automatically go in by song duration
for (int k = 0; k < arraySize; k++)
insert(myList, tunesInput[k]);
// should be sorted by duration
showList(myList);
// now do it again by title
myList.clear();
iTunesEntry::setSortType(iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_TITLE);
// build the list. It should automatically go in alphabetically by title
for (int k = 0; k < arraySize; k++)
insert(myList, tunesInput[k]);
// should be sorted by title
showList(myList);
return 0;
}
// Global method definitions --------------------------
void insert(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x)
{
list<iTunesEntry>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find a tune > x
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x < *iter )
break; // found the exact place for this float
myList.insert(iter, x);
}
bool remove(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x)
{
list<iTunesEntry>::iterator iter;
// loop until we find or exhaust list
for (iter = myList.begin() ; iter != myList.end() ; iter++ )
if ( x == *iter )
{
myList.erase(iter);
return true;
}
return false;
}
void removeAll(TunesList &myList, iTunesEntry x)
{
// if we wanted to return a bool true if found, we'd need to iterate
// just to detect a first occurence. But we'll let this be void
// and not worry about detecting x.
myList.remove(x);
}
void showList(TunesList &myList)
{
list<iTunesEntry>::iterator iter;
cout << endl << "_____Here's the List_______" << endl;
for( iter = myList.begin(); iter != myList.end(); iter++)
{
cout << "[" << iter->toString() << "] " << endl;
}
cout << endl << "_____That's all!_______" << endl << endl;
}
// iTunesEntry methods ---------------------------------------------------
// define static constants
int const iTunesEntry::MIN_STR_LENGTH = 1;
int const iTunesEntry::MAX_STR_LENGTH = 80;
int const iTunesEntry::MIN_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC = 1;
int const iTunesEntry::MAX_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC = 60*60; // 1 hour
int const iTunesEntry::DEFAULT_PLAY_TIME = 1; // 1 second
string const iTunesEntry::DEFAULT_STRING = " (undefined) ";
iTunesEntry::SortType iTunesEntry::sortKey = iTunesEntry::SORT_BY_ARTIST;
iTunesEntry::iTunesEntry()
{
title = DEFAULT_STRING;
artist = DEFAULT_STRING;
totalTime = DEFAULT_PLAY_TIME;
}
iTunesEntry::iTunesEntry(string nm, string art, int tTime)
{
if ( !setTitle(nm) )
title = DEFAULT_STRING;
if ( !setArtist(art) )
artist = DEFAULT_STRING;
if ( !setTotalTime(tTime) )
totalTime = DEFAULT_PLAY_TIME;
}
bool iTunesEntry::setTitle(string ttl)
{
if (ttl.length() < MIN_STR_LENGTH || ttl.length() > MAX_STR_LENGTH)
return false;
title = ttl;
return true;
}
bool iTunesEntry::setArtist(string art)
{
if (art.length() < MIN_STR_LENGTH || art.length() > MAX_STR_LENGTH)
return false;
artist = art;
return true;
}
bool iTunesEntry::setTotalTime(int tTime)
{
if (tTime < MIN_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC || tTime > MAX_PLAY_TIME_IN_SEC)
return false;
totalTime = tTime;
return true;
}
string iTunesEntry::toString()
{
ostringstream cnvrt;
cnvrt << "\"" << title << "\", by " << artist
<< " Duration: " << totalTime ;
return cnvrt.str();
}
bool iTunesEntry::setSortType( iTunesEntry::SortType which_type )
{
switch (which_type)
{
case SORT_BY_TITLE:
case SORT_BY_ARTIST:
case SORT_BY_TIME:
sortKey = which_type;
return true;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
int iTunesEntry::compareTo(iTunesEntry &other)
{
string thisName, otherName;
switch (sortKey)
{
case SORT_BY_TITLE:
if (title < other.title) // < already defined for string
return -1;
else if (other.title < title)
return +1;
else
return 0;
break;
case SORT_BY_ARTIST:
// get last name from string
// stack the last name before the first - no worries about trailing last nm
thisName = getArtistLastName() + artist;
otherName = other.getArtistLastName() + other.getArtist();
if (thisName < otherName) // < already defined for string
return -1;
else if (otherName < thisName)
return +1;
else
return 0;
break;
case SORT_BY_TIME:
return (totalTime - other.totalTime);
break;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
string iTunesEntry::getArtistLastName()
{
// search for first blank from end of string
// assume no trailing spaces
string ret_string;
int k, length;
length = artist.length();
if ( length < 1 )
return "";
for (k = length-1; k >= 0; k--)
{
if (artist[k] == ' ')
break;
}
if (k >= length-1 )
return "";
return artist.substr(k + 1, artist.length()-1 - k);
}
bool operator< (iTunesEntry &me, iTunesEntry &other)
{
return me.compareTo(other) < 0;
}
// don't use & because stl wants == overloaded with val, not ref param
bool operator==(iTunesEntry me, iTunesEntry other)
{
if ( me.getTitle() != other.getTitle() )
return false;
if ( me.getArtist() != other.getArtist() )
return false;
if ( me.getTotalTime() != other.getTotalTime() )
return false;
return true;
}